PRECOMMISSIONING OPERATIONS

SPECIAL FOCUS ON PIPELINES PRECOMMISSIONING OPERATIONS
For over 30 years, INTECNA has developed and applied products that are used in the pipeline hydraulic test phase. Our products have been approved by many Oil & Gas Companies, have been accepted in the discharge phase by Environmental Control Authorities around the World and have therefore received many references that identified INTECNA as an international player.
Many of the pipelines pre-commissioning activities are necessary to ensure that a newly laid pipeline is fully prepared for handover to its operator. Once a pipeline has been constructed, usually, the following tasks are undertaken to ensure suitability for use:
ELETROCOAGULATION PROCESS CRITICAL PARAMETERS
In relation to a hydro test operation, two main factors catalyse corrosion on steel surface and create eventual pipeline damage.
• Bacteria Present in the water
• Dissolved Oxygen
Hydrostatic test waters may provide a number of additives, depending upon the nature of the source water, the time of year of testing and other case specific factors.
Additives used in pipeline hydraulic test may include biocides, corrosion inhibitors, oxygen scavengers and leak detection tracers.
Biocides may be added to hydrostatic test waters to kill microorganisms. This may be required to prevent corrosion of the pipeline by sulphate reducing bacteria during testing
Corrosion inhibitors are not often added to hydrostatic test waters to prevent corrosion during testing, because the test water is only in the pipeline for a short period and the opportunity for corrosion is limited. Use of such additives is suggestible only for long residence time
Oxygen scavengers may be used to prevent pipeline corrosion.
Pipeline dewatering and Pipeline drying after the successful hydro-test, given that water a lead to corrosion or hydrates, this task is critical and must be performed efficiently.
The purpose of dewatering is to remove the initial fill/pre-commissioning fluid to prepare for introducing product to the pipeline system or to make the pipeline system ready for drying,
The purpose of drying is the removal of any water left in the pipeline after the dewatering operation in order to:
— prevent corrosion
— avoid hydrate formation
— prevent transport product contamination.
chemicals

• CORROSION INHIBITOR FOR SEA AND FRESH WATER
• BIOCIDES
• ALL IN ONE PRODUCTS (COCKTAIL TREATMENT)
• OXYGEN SCAVENGERS
• DYE TRACER
Services

• EVALUATION OF THE PROJECT IN ALL ASPECTS (Dimension, Metallurgy, Residence time, Operation etc.)
• EVALUATION OF ANALYTICAL WATER PARAMETER
• TECHNICAL PROPOSAL
• COMMERCIAL PROPOSAL AND PRODUCT SUPPLY
• SAFETY DOCUMENTATION IN TRANSPORT, STORAGE, HANDLING
• ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT EVALUATION
• TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE ON SITE
HIGH PRESSURE DOSAGE EQUIPMENT SUPPLY

Regarding PIPELINE DEWATERING OPERATION, it is well known that natural gas hydrates are clathrate compounds in which natural gas molecules are encased in cages of water molecules to form a solid ice-like substance.
Hydrate formation can restrict flow and even form a solid plug that can block all production in a short time period. This can cause failures, resulting in equipment damage, and possible injury and risks for workers. It is essential to implement a strategy to prevent or manage hydrates to avoid interruptions of the production cycle in a safe and cost-effective manner.
Methanol or Glycols (MEG – TEG) are normally used to dewater gas pipelines to prevent hydrate formation during the bulk dewatering phase of the commissioning process through stages that involve pigging ,air drying, vacuum drying and nitrogen packing.
In dewatering operations, Glycols are preferred. The problem associated with Glycols derives from their characteristics of Ignition Point (427 °C for MEG and 349° for TEG)
The characteristic of the auto-ignition point, involves the risk of explosion or fire in the presence of an undesired trigger, which can represent a potential danger for the operators and for the plant engineering structures.
Due to this reason, pig train must be propelled by N2
INTECNA offers a new solution to this issue and proposes a fluid to be used for the inhibition of hydrates (HYCOR HSI 600) , which has the following characteristics:
• absence of solvents or components that have a point of auto ignition,
• ability to prevent the formation of hydrates as thermodynamic inhibitor,
• control of the corrosion on the pipeline surface,
• possibility of discharge at sea without impact on the ecosystem (PLONOR LIST),
• possibility to use AIR instead Nitrogen for pig train propelling,
• easier handling without risks for the operators.
Achieving the ideal dryness for a subsea natural gas pipeline is a crucial step not only for the commissioning of a pipeline, but also for its subsequent integrity management. Attaining the correct dryness level can help inhibit microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) and especially further hydrates formation.
INTECNA’s program for hydro-test chemical treatment provides
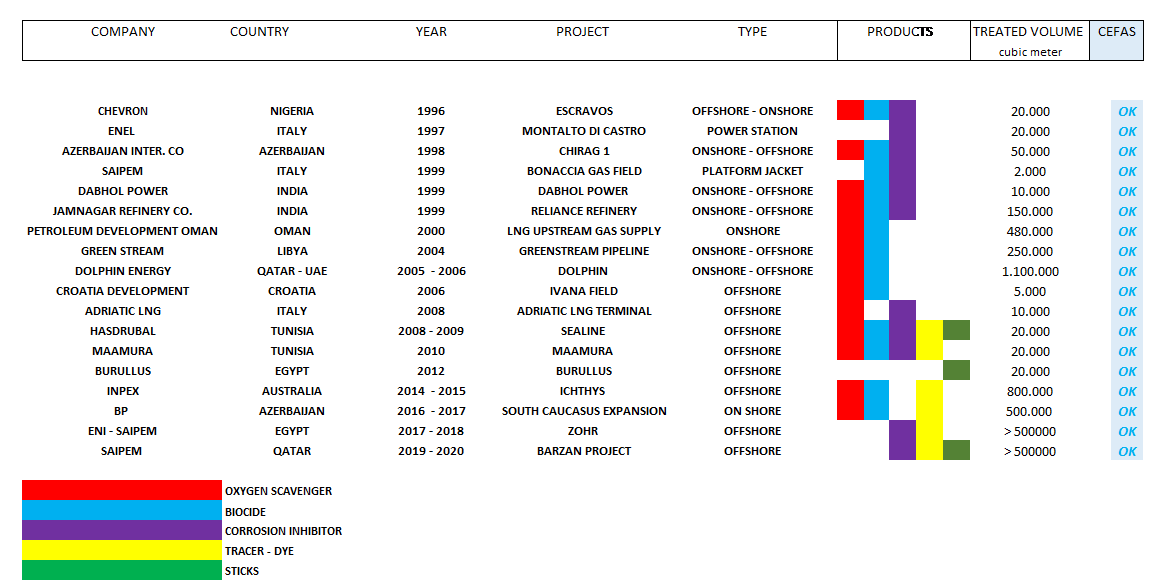
REFERENCE LIST and PROJECTS
TOP
©, Intecna Srl | Website created by Grazioli Design "Only for Dreamers"
